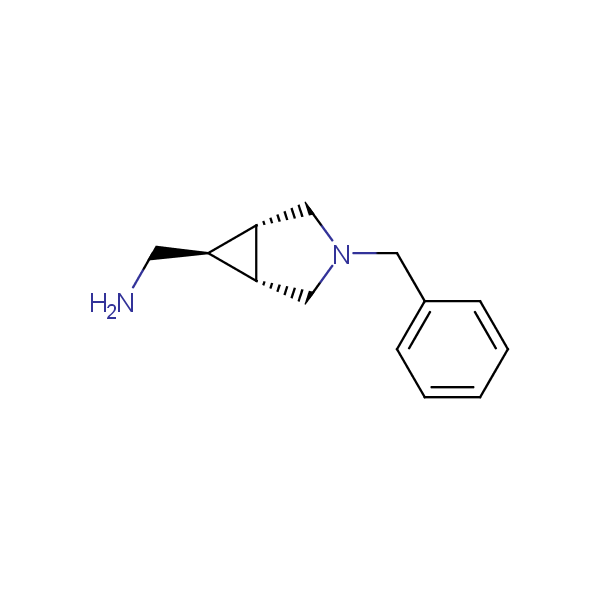
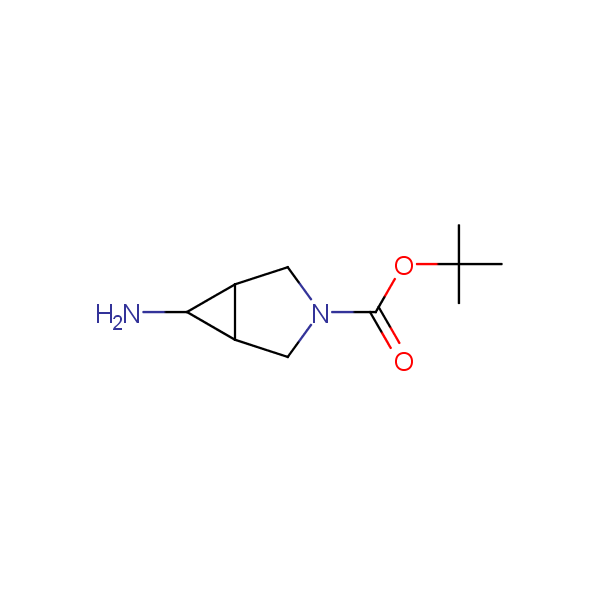
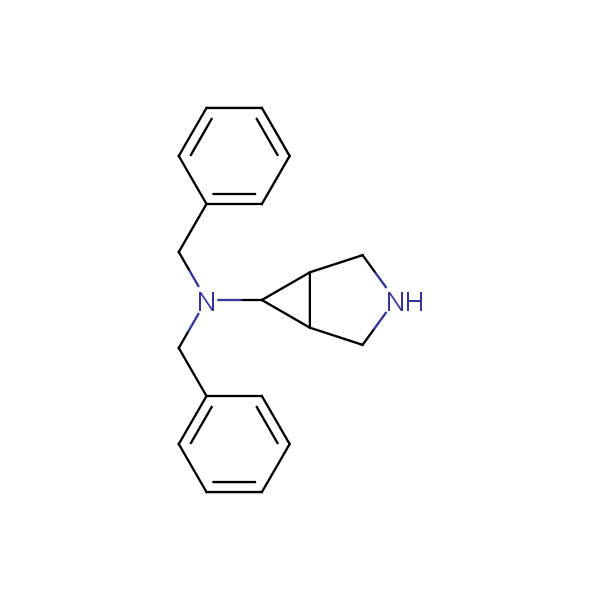
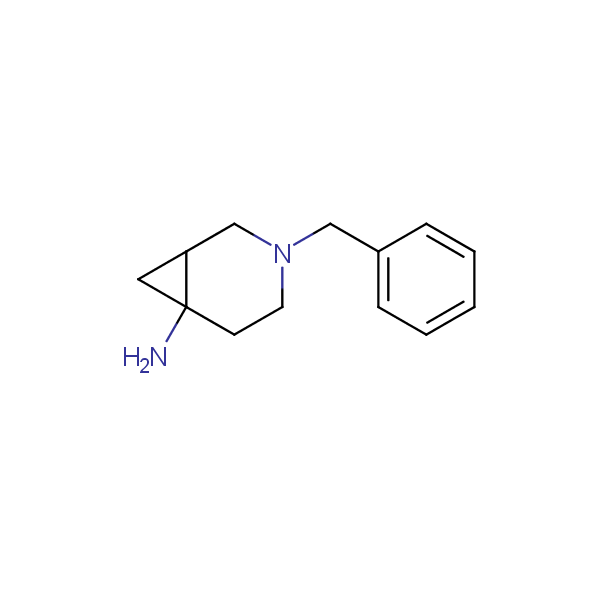
Conformationally restricted diamines and amino alcohols
The primary structure of a peptide can be formally considered as a oligoethylenediamine molecular platform to which the side chains and carbonyl oxygen atoms are attached through single and double bonds respectively. This backbone is conformationally restrained at the amide bonds and has some rotational degrees of freedom at single C-C and C-N bonds. The later become restricted upon the formation of the secondary structures stabilized by multiple hydrogen bonds. The fragments of 1,3-, 1,4-, 1,5- and 1,6-diamines are found in peptides containing aspargine, glutamine, tryptophane, histidine, lysine and arginine. Apparently some structural, conformational and functional features of peptides can be reproduced by designed derivatives of synthetic conformationally restrained diamines.
The primary structure of a peptide can be formally considered as a oligoethylenediamine molecular platform to which the side chains and carbonyl oxygen atoms are attached through single and double bonds respectively. This backbone is conformationally restrained at the amide bonds and has some rotational degrees of freedom at single C-C and C-N bonds. The later become restricted upon the formation of the secondary structures stabilized by multiple hydrogen bonds. The fragments of 1,3-, 1,4-, 1,5- and 1,6-diamines are found in peptides containing aspargine, glutamine, tryptophane, histidine, lysine and arginine. Apparently some structural, conformational and functional features of peptides can be reproduced by designed derivatives of synthetic conformationally restrained diamines.
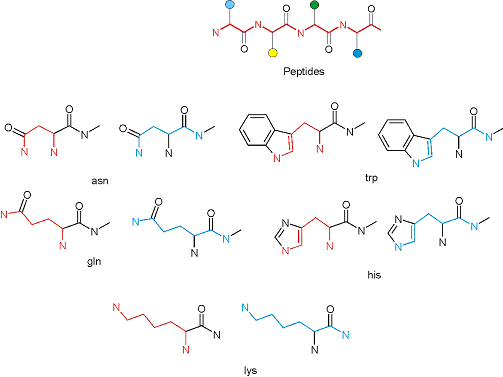
Diamine units in peptides.
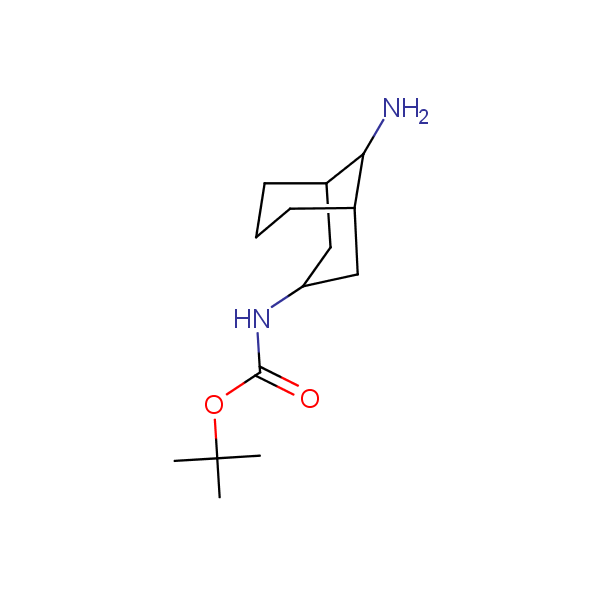
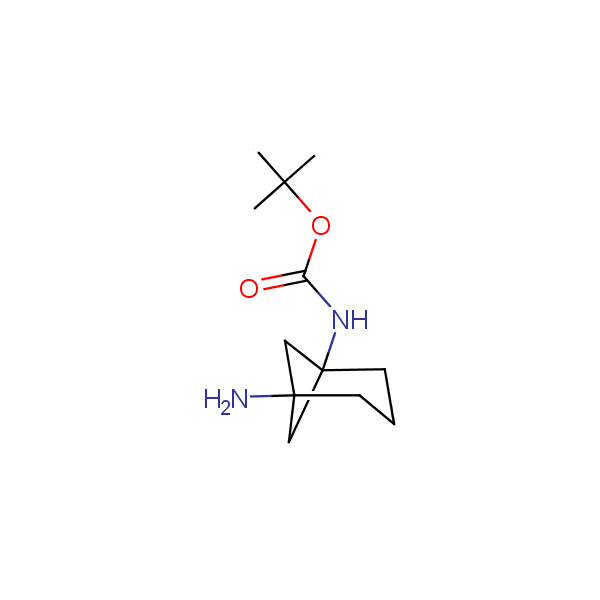
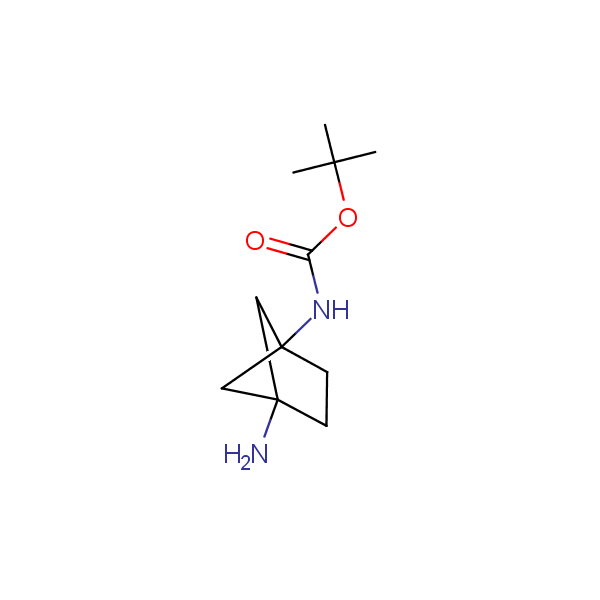
Recently, Enamine has initiated an in-house project focusing on multigram scale syntheses of known and novel conformationally restricted monoprotected diamines and amino alcohols which can be used as molecular scaffolds in rational design of drugs and peptidomimetics bearing two different functional groups in well defined spatial arrangements.
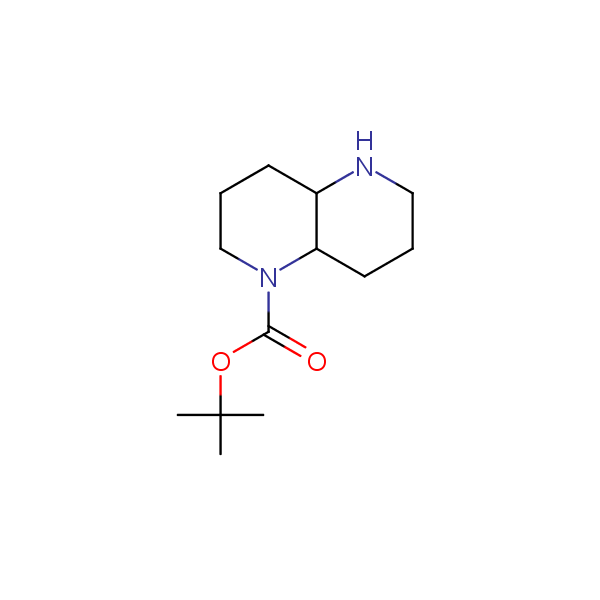
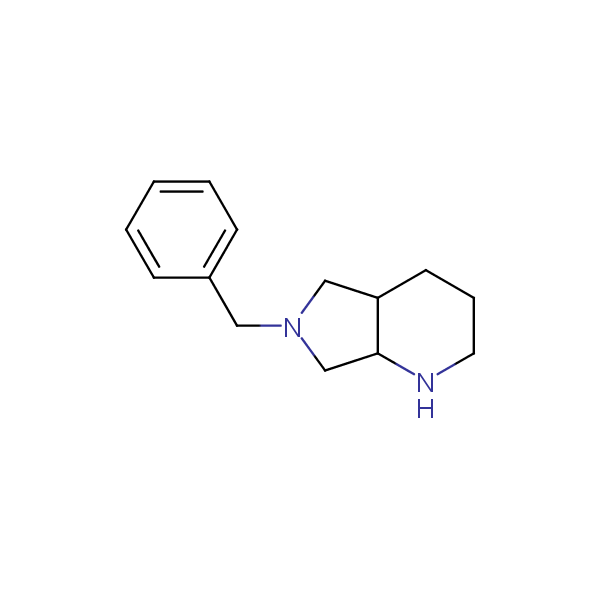
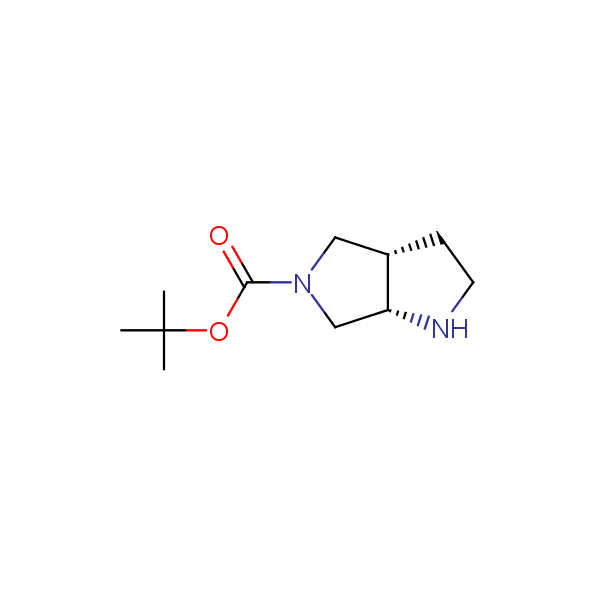
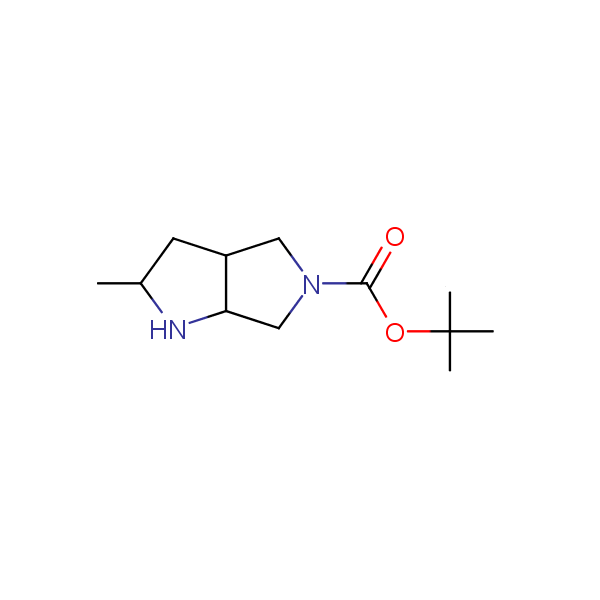
Our minilibrary of monoprotected conformationally restricted cyclic diamines comprises molecules containing 1,2- or 1,3-diamine units adopting anti- configuration. The arrangement of amino groups in these diamines is similar to that in peptide chains of the -sheet secondary structures. High level of preorganization and low conformational mobility are distinguishing characteristics of many bicyclic compounds containing units of 1,2-, 1,3- and 1,4-diamines. The arrangement of amino groups in some molecules is virtually constrained whereas structures of other proposed diamines allow certain rotational degrees of freedom.
A set of conformationally constrained diamine building blocks is proposed either from stock or for re-synthesis.
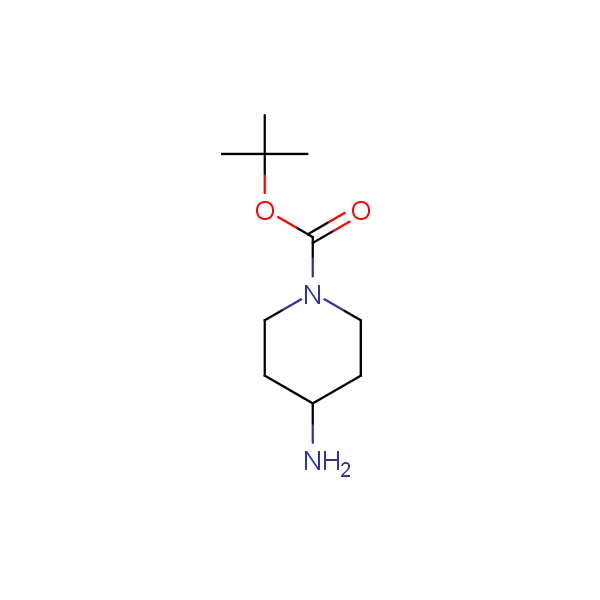
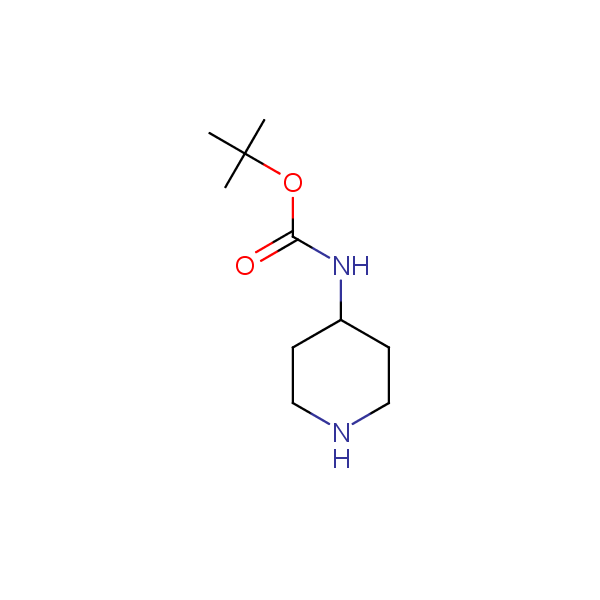
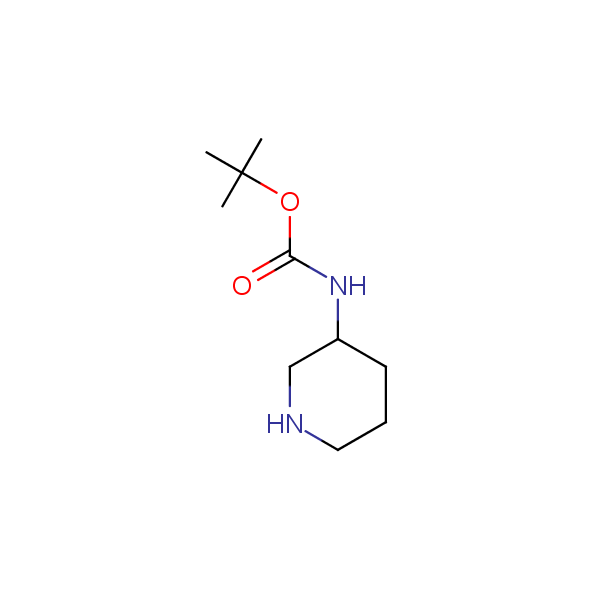
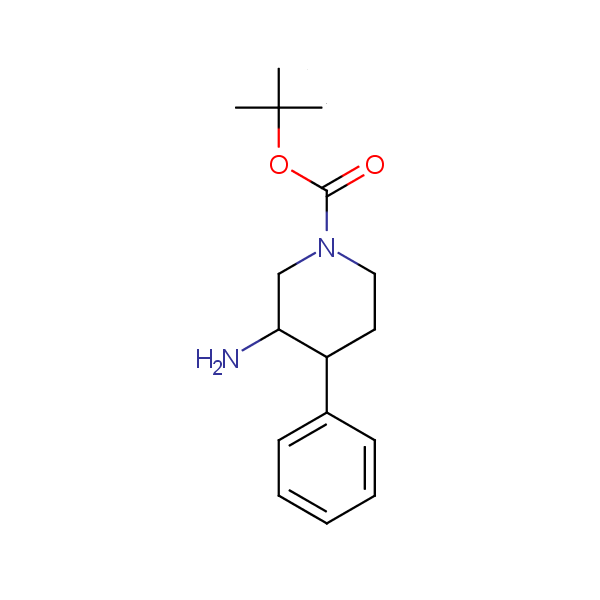
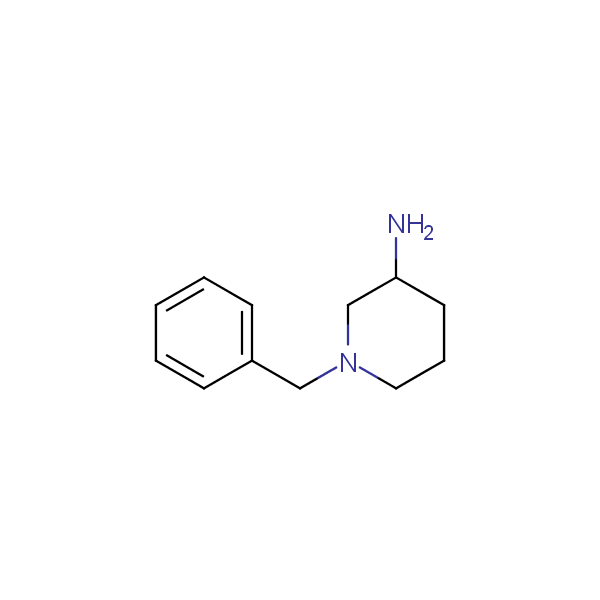
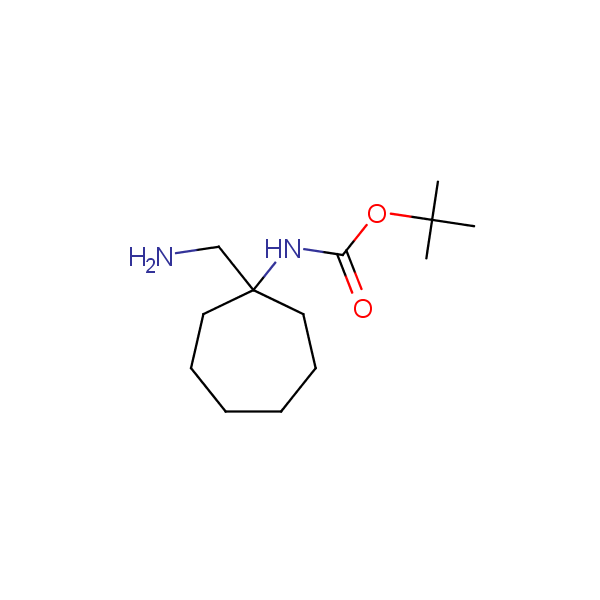
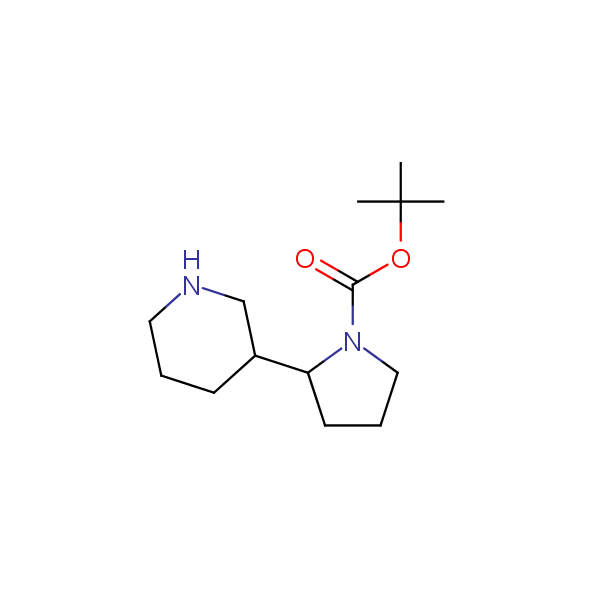
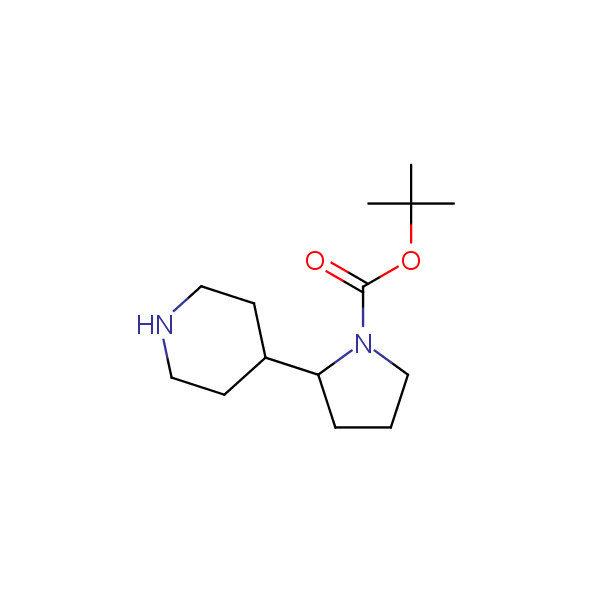
Monocyclic diamines
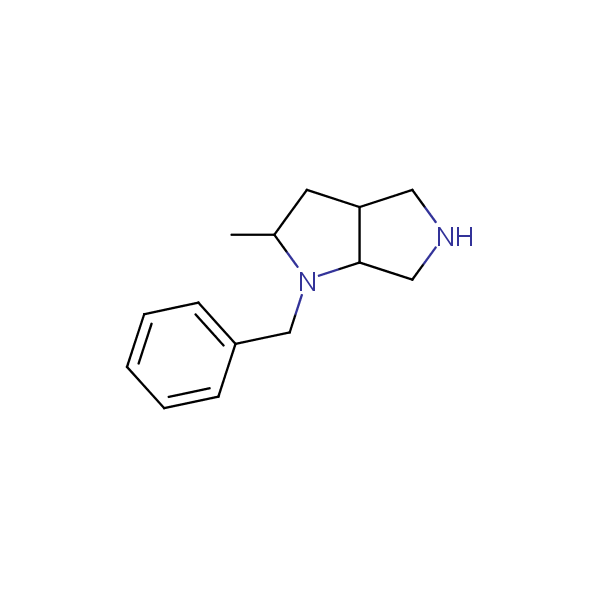
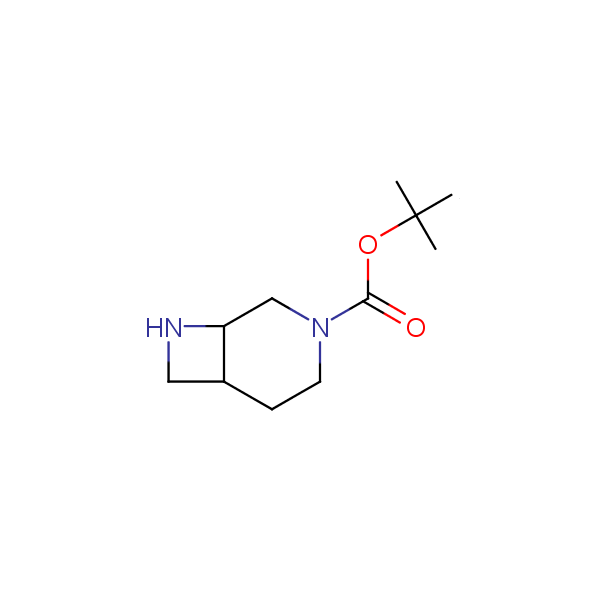
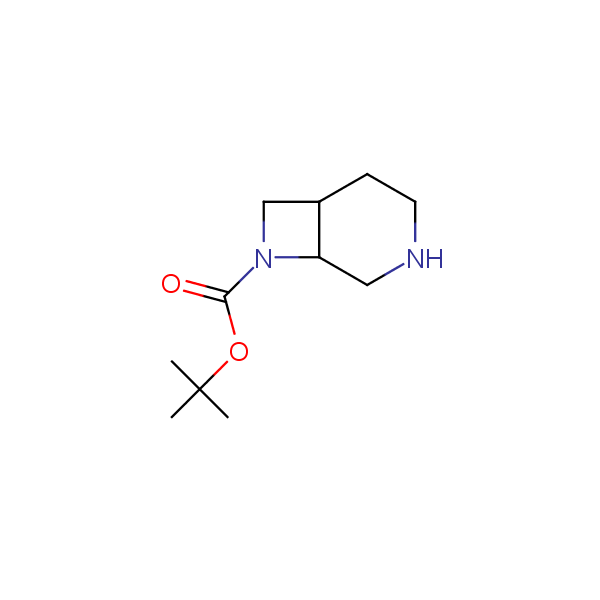
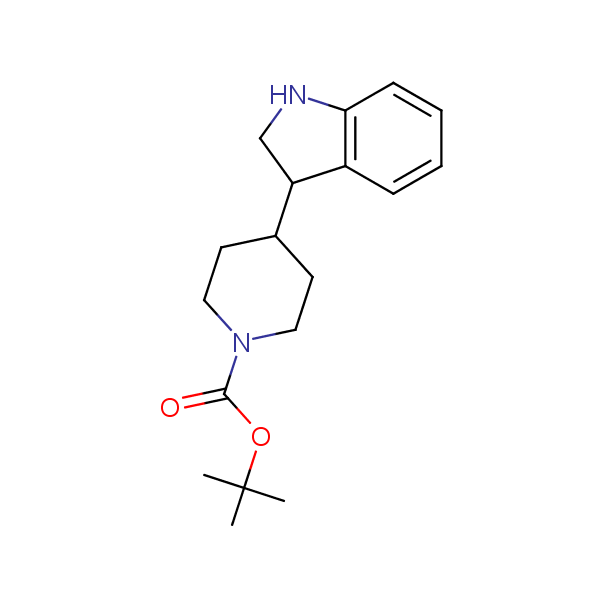
Bicyclo[m.n.0]alkane diamines
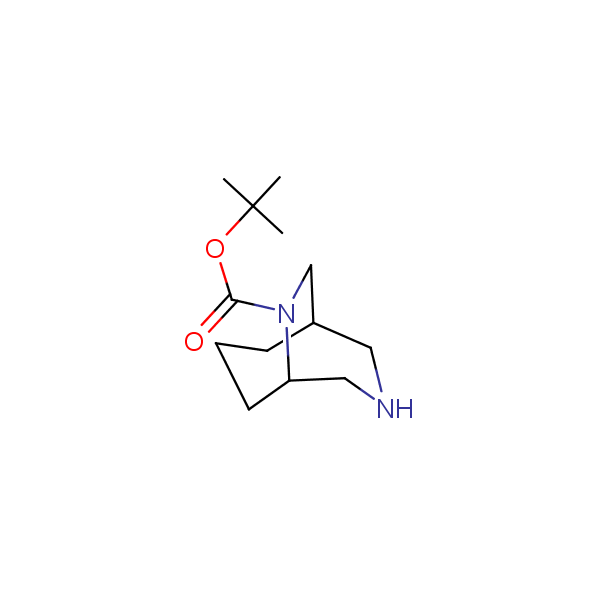
Other Bicyclo[m.n.k]alkane diamines
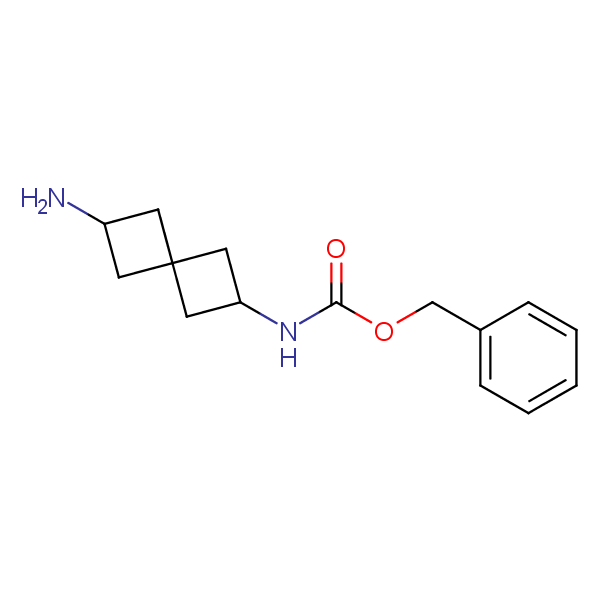
Spiroalkane diamines
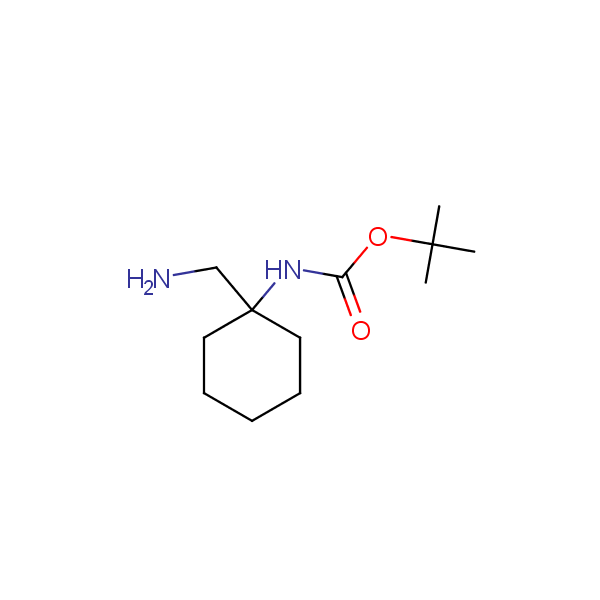
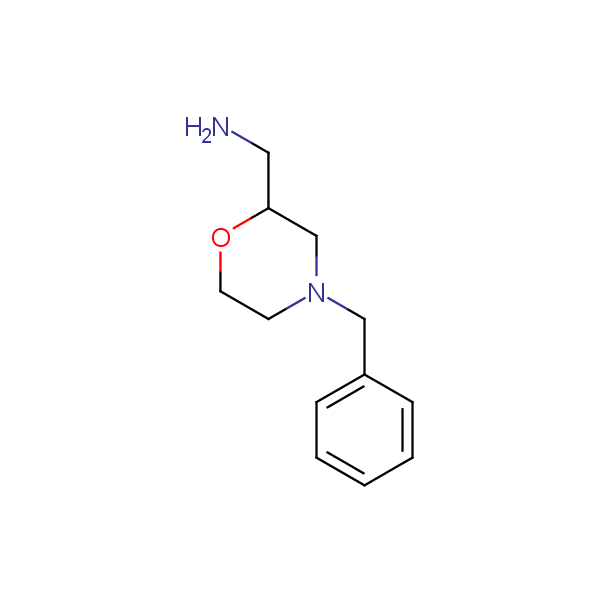
Other diamines
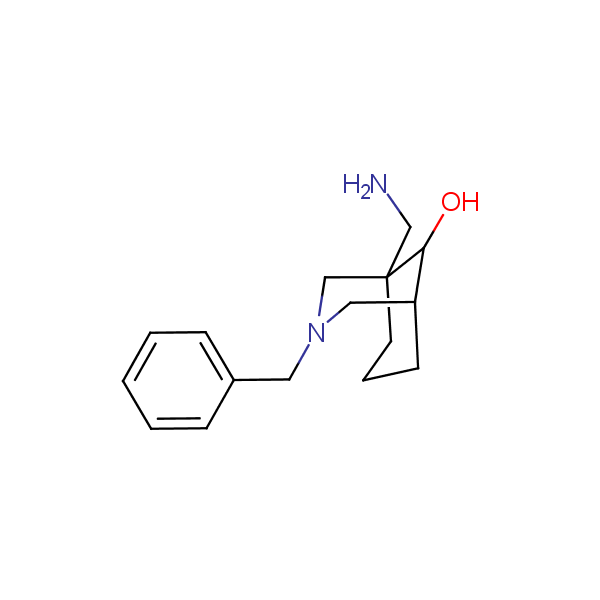
Conformationally restricted amino alcohols. All products are >96% chemically pure, and >95% (mostly > 99%) optically pure.